这是学习Deep Learning.tv - Deep Learning SIMPLIFIED的系列视频,自己总结出的学习笔记。 转载请注明:“转载自zyddora.github.io”
Catalog
- our choice of Deep Net Ep4
- An Old Problem Ep5
- Restricted Boltzmann Machines Ep6
- Deep Belief Nets Ep7
- Convolutional Nets Ep8
- Recurrent Nets Ep9
- Autoencoders Ep10
- Recursive Neural Tensor Nets Ep11
- Use Cases Ep12
our choice of Deep Net Ep4
-
Unlabeled: feature extraction; unsupervised learning; pattern recognition, use RBM; Autoencoders.
-
Labeled: Text processing (sentiment analysis; parsing; named entity recognition), use: RNTN (Recursive Neural Tensor Network) or RNN (Recurrent Net), especially for language model works on character level. Image Recognition, use: DBN (Deep Belief Network) or CNN (Convolutional Net). Object Recognition, use: RNTN or Convolutional Net. Speech Recognition, use: Recurrent Net.
An Old Problem Ep5
Back propagation occurs a vanishing gradient problem—training takes too long and accuracy suffers. The gradients are much smaller in the earlier layers, as a result, these layers are the slowest to train.
Restricted Boltzmann Machines Ep6
"What allowed to overcome vanishing gradient? " — 2 parts
The 1st part: RBM, by Geoff Hinton.
Structure:A shallow two layered net.
Why RESTRICTED? — No two nodes in the same layer share a connection.
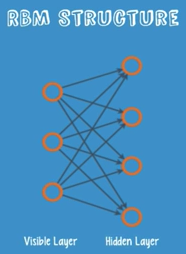
Several forward and backward passes — reconstruct the input data. 3 steps:
- With a forward pass, every input is combined with an individual weight and overall bias, and the result is passed to the hidden layer which may or may not activate.
- Next, in the backward pass, each activation is combined with an individual weight and an overall bias, and the result is passed to the visible layer for reconstruction.
- At the visible layer, the reconstruction is compared against the original input to determine the quality of the result. RBMs use a measure called KL Divergence (KL散度)for step 3; 1 through 3 are repeated with varying weights and biases until the input and the reconstruction are as close as possible.
The data doesn’t need to be labelled. An RBM is actually making decisions about which input features are important and how they should be combined to form patterns. In other words, an RBM is part of a family of feature extractor neural nets, which are designed to recognize inherent patterns in data. These nets are also called autoencoders.
Deep Belief Nets Ep7
"What allowed to overcome vanishing gradient? " — 2 parts
Another part: DBN, by Geoff Hilton also. The network structure of DBN is identical to an MLP. But when it comes to training, they are entirely different.
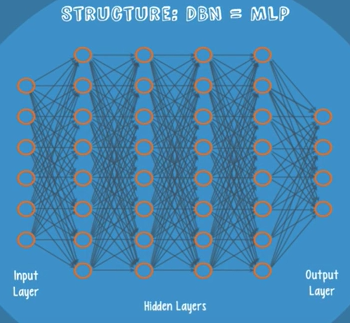
DBN can be viewed as a stack of RBMs. A DBN is trained as follows:
- The first RBM is trained to reconstruct it’s input as accurately as possible.
- The hidden layer of the first RBM is treated as the visible layer for the second and the second RBM is trained using the outputs from the first RBM.
- This process is repeated until every layer in the network is trained. An important note: a DBN is that each RBM layer learns the entire input. It works globally be fine tuning the entire input in succession as the model slowly improves.
The benefits of DBN—a solution to the vanishing gradient problem!s
- Only needs a small labelled data set.
- The training process can be completed in a reasonable amount of time through the use of GPUs.
- The resulting net will be very accurate compared to a shallow net.
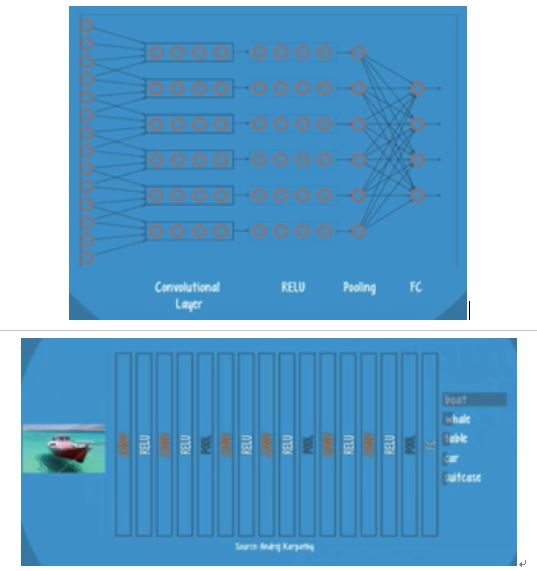
Convolutional Nets Ep8
CNN (Convolutional neural net): by Yann Lecun of NYU, dominant solution in image recognition.
Component layer to an CNN: A convolutional layer, RELU, and pooling layers—all of which are repeated several times.
Use GPUs to compute. Requires a large set of labelled data for training, which can be challenging to obtain in a real-world application.
CNNs are trained using back-prop, so the vanishing gradient problem is again a potential issue.
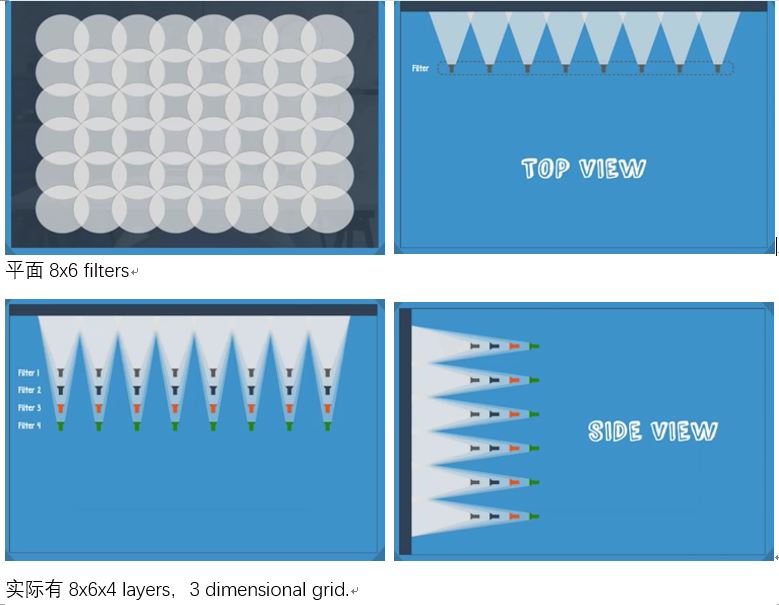
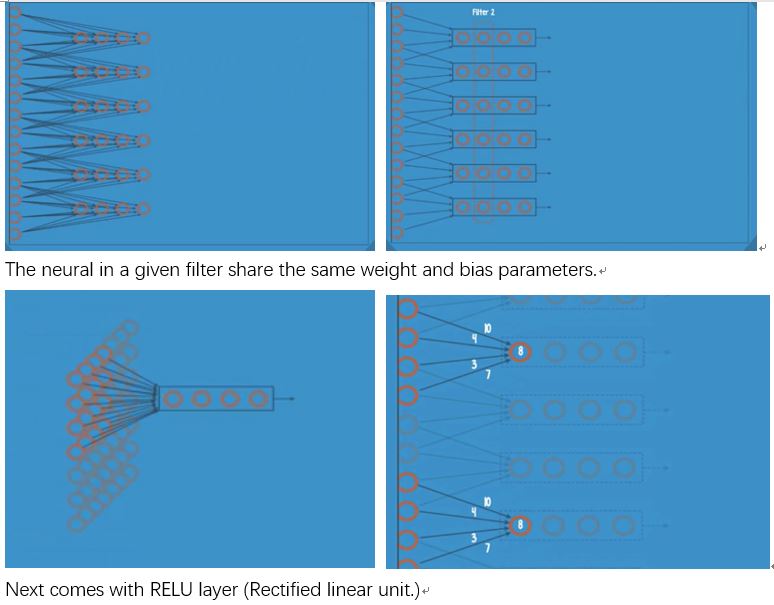
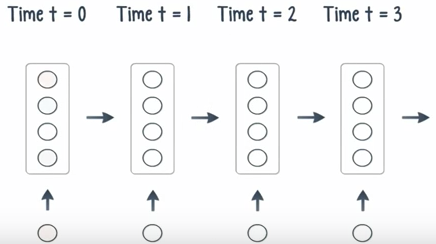
Recurrent Nets Ep9
If the patterns in data change with time, use a recurrent neural network.
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): by Juergen Schmidhuber, Sepp Hochreiter, and Alex Graves.
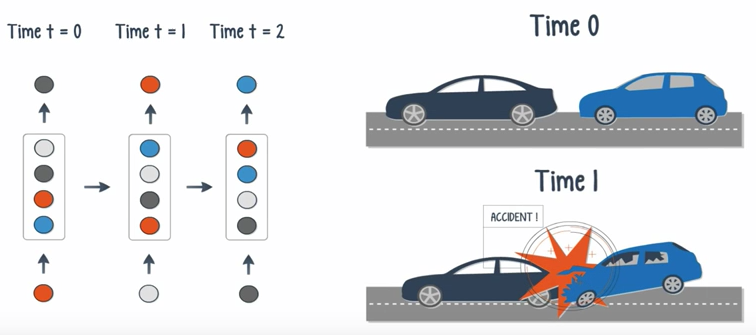
Unlike feedforward nets, in a recurrent net, the output of a layer is added to the next input and feed back into the same layer, which is typically the only layer in the entire network.
Think of it as a pass through time.
Applications:
- When the input is singular and the output is a sequence, a potential application is image captioning.
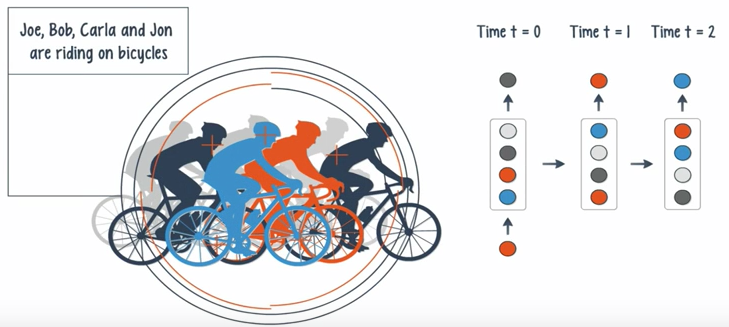
- A sequence of inputs with a single output can be used for document classification.
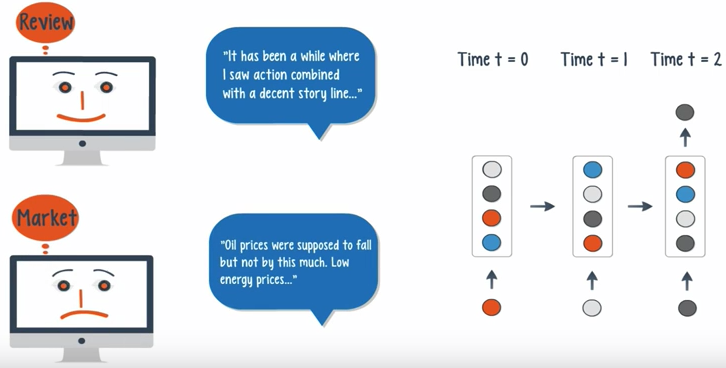
- When both the input and output are sequences, can classify videos frame by frame.
- If the time delay is introduced, the net can statistically forecast the demand in supply chain planning.
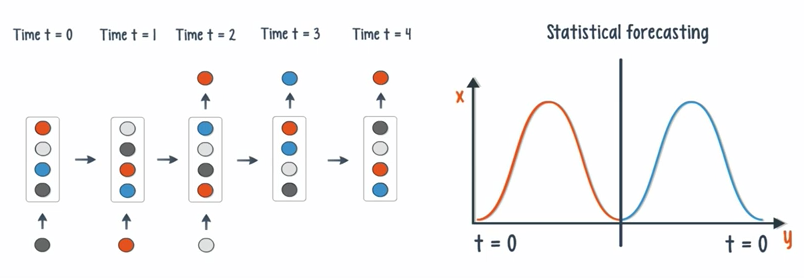
STACKING: By stacking RNNs on top of each other, you can form a net capable of more complex output than a single RNN working alone.
We once again run into the problem of vanishing gradient. Unfortunately, it is exponentially worse for an RNN. The reason is that each time step is equivalent of an entire layer in a feedforward networks. This leads to a small gradients and a decay of information through time.
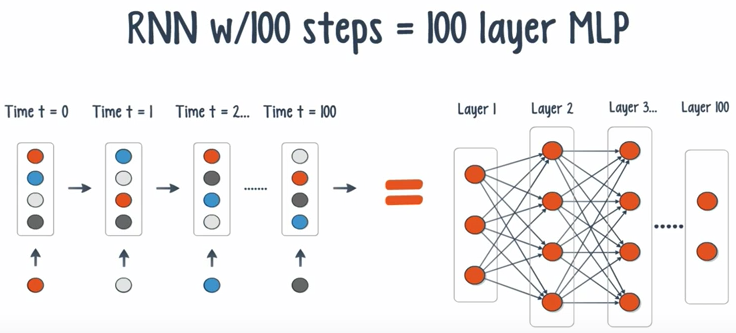
Several solutions:
- Gating units;
- Gradient clipping;
- Steeper Gates;
- Better optimizers. The most popular is Gating: which is a technique that helps the net decide when to forget the current input, and when to remember it for future time steps. The most popular gating types are GRU and LSTM. GPUs are an obvious choice to train a recurrent net.
"When to use a recurrent net over a feedforward net?" Feedforward net = Classifier / Regressor. (Class or prediction.) Recurrent net = Forecaster.
Autoencoders Ep10
Figure out the underlying structure of a data set, extract the features is useful when you start applying labels. Autoencoders are well suited for this task. (feature extraction engine)
shallow autoencoders:
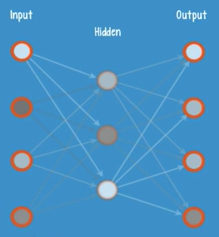
2 steps—the encoding and the decoding. Typically, the same weights that are used to encode a feature in the hidden layer are used to reconstruct an image in the output layer.
Autoencoders are trained with back-prop using a metric called "loss", which measures the amount of information that was lost when the net tried to reconstruct the input.
Deep autoencoders are useful tools for dimensionality reduction. It preforms better at dimensional reduction than their predecessor—PCA.
Recursive Neural Tensor Nets Ep11
RNTNs: by Richard Socher @MetaMind. To discover the hierarchical structure of a set of data, such as the parse trees of a group of sentences. They were designed for sentiment analysis.
Structure: — Form a binary tree.
3 basic components:
A parent group (root); Child groups (leaves); composed with neurons.
The root is connected to both leaves, but the leaves are not connected to each other.
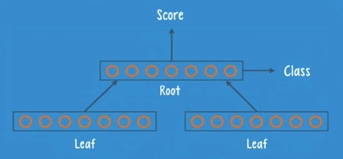
RNTNs are trained with backpropagation by comparing the predicted sentence structure with the proper sentence structure obtained from a set of labelled training data. Once trained, the net will give a higher score to structures that are more similar to the parse trees that it saw in training.
RNTNs are used in NLP for both syntactic parsing and sentiment analysis. They are also used to parse images, when an image contains a scene with many different components.
Use Cases Ep12
- Machine vision; Image classification; Object Recognition; Video Recognition; Speech Recognition;
- Fact extraction;
- Machine translation;
- sentiment analysis;
- Medical; Cancer detection; drug discovery;
- Radiology;
- Finance;
- Digital advertising;
- Fraud detection;
- Customer intel;
Youtube上仍在不断上传新视频,博主将会进一步关注,更新本文。