本文旨在介绍ARMv7开始增加的一项advanced SIMD extension——NEON技术。有助于帮助读者理解NEON概况,提供的实例分析有助于迅速上手NEON编程。阅读此文要求读者有基本的C/C++经验及汇编代码经验,若没有也没关系,多理解查阅资料即可。Good luck~!
Catalog
SIMD及NEON概览
SIMD
Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD)顾名思义就是“一条指令处理多个数据(一般是以2为底的指数数量)”的并行处理技术,相比于“一条指令处理几个数据”,运算速度将会大大提高。它是Michael J. Flynn在1966年定义的四种计算机架构之一(根据指令数与数据流的关系定义,其余还有SISD、MISD、MIMD)。
许多程序需要处理大量的数据集,而且很多都是由少于32bits的位数来存储的。比如在视频、图形、图像处理中的8-bit像素数据;音频编码中的16-bit采样数据等。在诸如上述的情形中,很可能充斥着大量简单而重复的运算,且少有控制代码的出现。因此,SIMD就擅长为这类程序提供更高的性能,比如下面几类:
- Block-based data processing.
- Audio, video, and image processing codes.
- 2D graphics based on rectangular blocks of pixels.
- 3D graphics.
- Color-space conversion.
- Physics simulations.
在32-bit内核的处理器上,如Cortex-A系列,如果不采用SIMD则会将大量时间花费在处理8-bit或16-bit的数据上,但是处理器本身的ALU、寄存器、数据深度又是主要为了32-bit的运算而设计的。因此NEON应运而生。
NEON
NEON就是一种基于SIMD思想的ARM技术,相比于ARMv6或之前的架构,NEON结合了64-bit和128-bit的SIMD指令集,提供128-bit宽的向量运算(vector operations)。NEON技术从ARMv7开始被采用,目前可以在ARM Cortex-A和Cortex-R系列处理器中采用。
NEON在Cortex-A7、Cortex-A12、Cortex-A15处理器中被设置为默认选项,但是在其余的ARMv7 Cortex-A系列中是可选项。NEON与VFP共享了同样的寄存器,但它具有自己独立的执行流水线。
NEON架构(数据类型/寄存器/指令集)
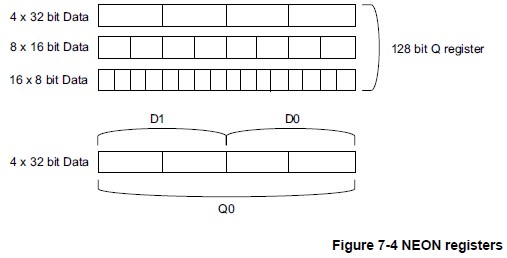
NEON支持的数据类型
- 32-bit single precision floating-point 32-bit单精度浮点数;
- 8, 16, 32 and 64-bit unsigned and signed integers 8, 16, 32 and 64-bit无符号/有符号整型;
- 8 and 16-bit polynomials 8 and 16-bit多项式。
NEON数据类型说明符:
- Unsigned integer U8 U16 U32 U64
- Signed integer S8 S16 S32 S64
- Integer of unspecified type I8 I16 I32 I64
- Floating-point number F16 F32
- Polynomial over {0,1} P8
注:F16不适用于数据处理运算,只用于数据转换,仅用于实现半精度体系结构扩展的系统。
多项式算术在实现某些加密、数据完整性算法中非常有用。
NEON寄存器(重点)
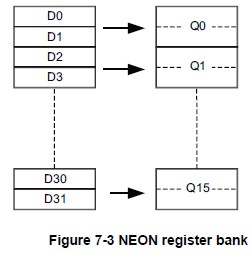
NEON寄存器有几种形式:
- 16×128-bit寄存器(Q0-Q15);
- 或32×64-bit寄存器(D0-D31)
- 或上述寄存器的组合。
注:每一个Q0-Q15寄存器映射到一对D寄存器。
寄存器之间的映射关系:
- D<2n> 映射到 Q
的最低有效半部; - D<2n+1> 映射到 Q
的最高有效半部;
结合NEON支持的数据类型,NEON寄存器有如下图的几种形态:
NEON 数据处理指令可分为:
- Normal instructions can operate on any vector types, and produce result vectors the same size, and usually the same type, as the operand vectors.
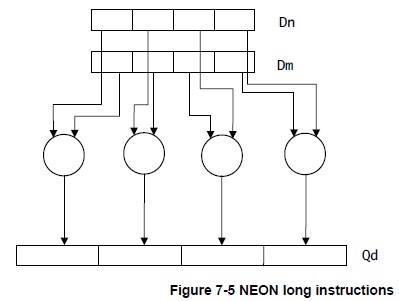
- Long instructions operate on doubleword vector operands and produce a quadword vector result.(操作双字vectors,生成四倍长字vectors) The result elements are usually twice the width of the operands, and of the same type.(结果的宽度一般比操作数加倍,同类型) Long instructions are specified using an L appended to the instruction.(在指令中加L)
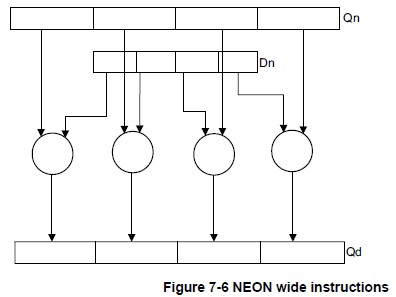
- Wide instructions operate on a doubleword vector operand and a quadword vector operand, producing a quadword vector result.(操作双字 + 四倍长字,生成四倍长字) The result elements and the first operand are twice the width of the second operand elements.(结果和第一个操作数都是第二个操作数的两倍宽度) Wide instructions have a W appended to the instruction.(在指令中加W)
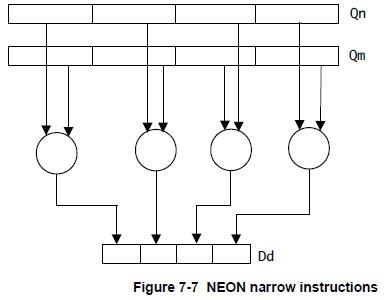
- Narrow instructions operate on quadword vector operands, and produce a doubleword vector result.(操作四倍长字,生成双字) The result elements are usually half the width of the operand elements.(结果宽度一般是操作数的一半) Narrow instructions are specified using an N appended to the instruction.(在指令中加N)
- Saturating variants
- ARM中的饱和算法:
- 对于有符号饱和运算,如果结果小于 –2^n,则返回的结果将为 –2^n;
- 对于无符号饱和运算,如果整个结果将是负值,那么返回的结果是 0;如果结果大于 2^n – 1,则返回的结果将为 2^n – 1;
- NEON中的饱和算法:通过在V和指令助记符之间使用Q前缀可以指定饱和指令,原理与上述内容相同。
- ARM中的饱和算法:
下面给出几幅图解释上述指令的操作原理,图片来自Search Results Cortex-A Series Programmer’s Guide
NEON指令集(重点)
ARMv7/AArch32指令格式
所有的支持NEON指令都有一个助记符V,下面以32位指令为例,说明指令的一般格式:
V{<mod>}<op>{<shape>}{<cond>}{.<dt>}{<dest>}, src1, src2
- <mod>
- Q: The instruction uses saturating arithmetic, so that the result is saturated within the range of the specified data type, such as
VQABS,VQSHLetc. - H: The instruction will halve the result. It does this by shifting right by one place (effectively a divide by two with truncation), such as
VHADD,VHSUB. - D: The instruction doubles the result, such as
VQDMULL,VQDMLAL,VQDMLSLandVQ{R}DMULH. - R: The instruction will perform rounding on the result, equivalent to adding 0.5 to the result before truncating, such as
VRHADD,VRSHR.
- Q: The instruction uses saturating arithmetic, so that the result is saturated within the range of the specified data type, such as
- <op> - the operation (for example,
ADD,SUB,MUL). - <shape> - Shape,即前文中的Long (L), Wide (W), Narrow (N).
- <cond> - Condition, used with IT instruction.
- <.dt> - Data type, such as s8, u8, f32 etc.
- <dest> - Destination.
- <src1> - Source operand 1.
- <src2> - Source operand 2.
注: {} 表示可选的参数。
比如:
VADD.I16 D0, D1, D2 @ 16位加法
VMLAL.S16 Q2, D8, D9 @ 有符号16位乘加
NEON支持的指令总结
- 运算:和、差、积、商
- 共享的 NEON 和 VFP 指令:涉及加载、多寄存器间的传送、存储
具体指令请参见ARM® Compiler armasm User Guide - Chapter 12 NEON and VFP Instructions
注:VFP指令与NEON可能相像,助记符也可能与NEON指令相同,但是操作数等等是不同的,涉及多个基本运算。